Electrifying Liard River Hot Springs

History of Conflict
Although the source of the springs is natural, the pools were built during the construction of the Alaska Highway during World War II. The location is an extremely remote section of the road and is surrounded by undisturbed wilderness. The geothermal-supported microclimate is vibrant and the valley is extremely productive for black bears and other wildlife. Bears have even been observed to soak in the hot pools themselves.
The hot pools are the second largest in Canada and are the only major attraction for hundreds of miles so many travelers on the Alaska Highway stop for a soak or to camp. The combination of concentrated bear population and non-natural attractants made this a heavy conflict zone.
Unfortunately, this deadly combination resulted in two human fatalities in 1997. Partially as a result of this history, lethal control was often used as a primary mitigation strategy for human-bear conflict.
Construction
Site Size
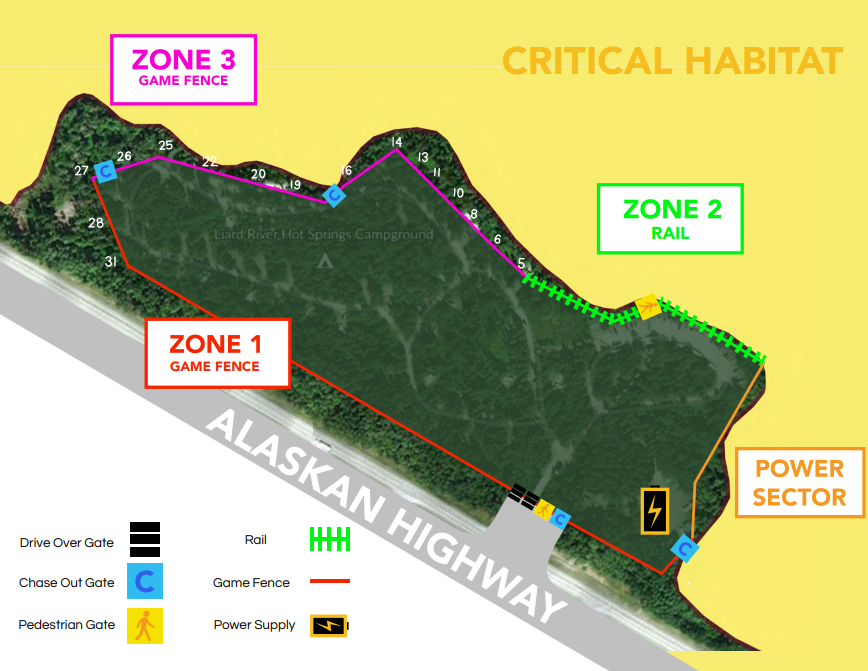
The total fence line was surveyed at 1600 meters. This is a moderately large electric fence in total distance. Adding substantial grounding and breaking the fence into two separately energized sections ensured an effective shock would be delivered at any spot on the fence.
Vehicle Access
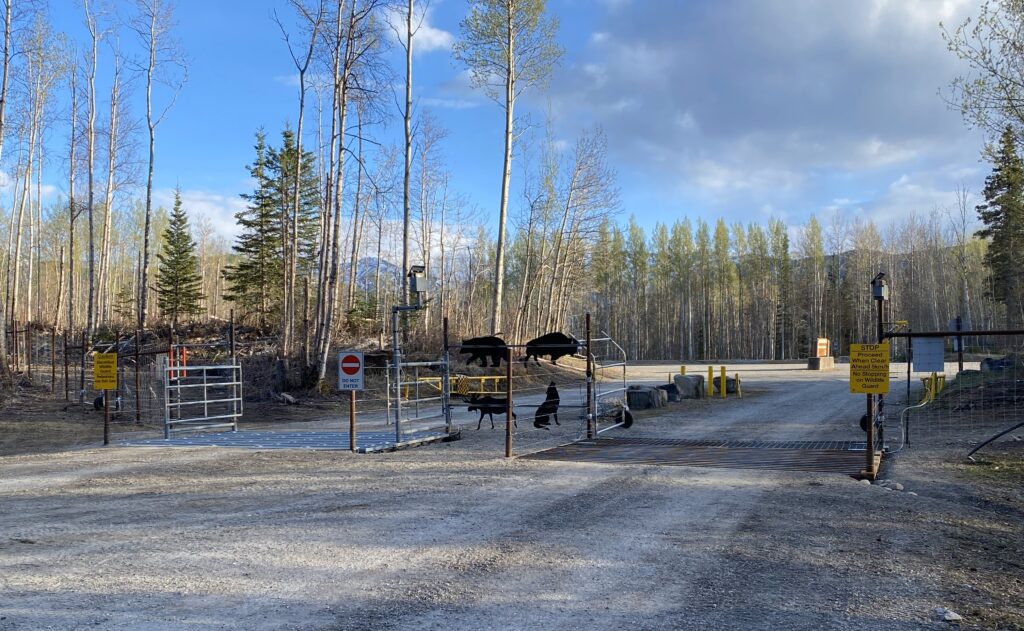
A fence must simultaneously exclude animals while allowing easy human access. The requirement for easy and frequent vehicle access demanded a more user-friendly solution than a simple gate. A custom-designed electrified wildlife guard (similar to a cattle- guard) was designed and installed to allow un-restricted vehicle access while excluding animals.
Fence Line Selection
The fence was constructed around the perimeter of the park facilities, camping, and day-use areas, with all visitor parking contained within the fence. As the campground was already constructed, there was little room between the camping pads and the wetland area which is the Department of Fisheries designated critical habitat for endemic snails. Precision surveying, fencing preparation, and 31 direction changes along the fence line allowed construction within these constraints.
Fence Line Preparation
Much of the fence line was located in heavily forested areas. It is important that a fence line is prepared both for construction as well As for ongoing monitoring. Wildlife should have a chance to clearly see a fence through a cleared area rather than bumping into a fence in the midst of heavy forest. We used an industrial mulcher to clear the right-of-way, which also helps in suppressing vegetative regrowth. As the area has had indigenous use, an archaeologist supervised construction and identified a number of culturally modified trees.
Visual Impact on park Guests
Electric fencing can be intimidating for anyone who is not experienced in dealing with them. The fence was designed to remain visually appealing while also including necessary signage to ensure proper use of the fencing system. The fencing around the picnic site was made out of wood rail material with electric fence outrigging to maintain park aesthetics in the most visible areas of the fence line.